Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
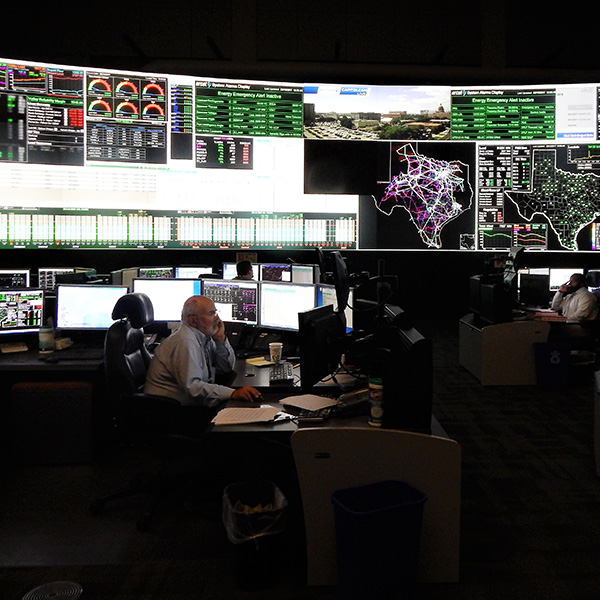
ERCOT surprised market participants with an announcement that it plans to increase operating reserves by requesting an additional 3,000 MW of capacity to shore up the grid for the upcoming winter.
A call for FERC to run a technical conference on capacity accreditation ran into a mixed reception, with the ISO/RTO Council saying it is too regional of an issue for the idea to have an impact.
Doubts continue to swirl around which version of MISO’s future fleet mix is appropriate for long-range transmission planning — the Independent Market Monitor’s or the RTO’s itself.
Senior executives from all seven ISO/RTOs discussed how the changing resource mix is impacting reliability.
PJM's Board of Managers has adopted a variant of the RTO annual capacity market CIFP proposal, which includes changes to risk modeling, accreditation and capacity performance.
PJM members recommended various avenues for the RTO's Board of Managers to consider as it weighs a possible FERC filing incorporating components of proposals made during the critical issue fast path process.
CAISO’s issuance of energy emergency watches and alerts in July came under conditions that mirrored those during California’s September 2022 heatwave.
MISO says it continues research to gauge the quantity of generating attributes it might prescribe for its fleet.
ERCOT says it should have more than enough capacity to meet peak demand under normal conditions during the fall season that begins in October.
MISO officials said they probably could have held off their decision to call a summertime emergency in late August.
Want more? Advanced Search