winter reliability
The North American grid made it through the winter storm of Jan. 24-26 — dubbed “Fern” by The Weather Channel — relatively unscathed, but the cold weather gripping much of the U.S. and Canada continues, and cold snaps in the future will still stress the interconnected power and natural gas systems.
As extreme winter weather descended on the Eastern U.S. and Canada, Hydro-Québec suspended power exports to New England on the New England Clean Energy Connect transmission line because of reliability concerns in Québec.
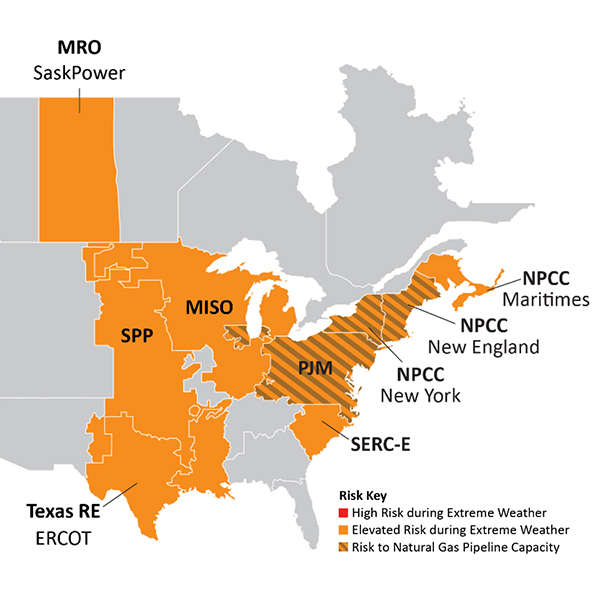
WECC expects two regions to be under elevated risk as the West heads into the winter, with staff saying a prolonged weather event could impact operating reserves.
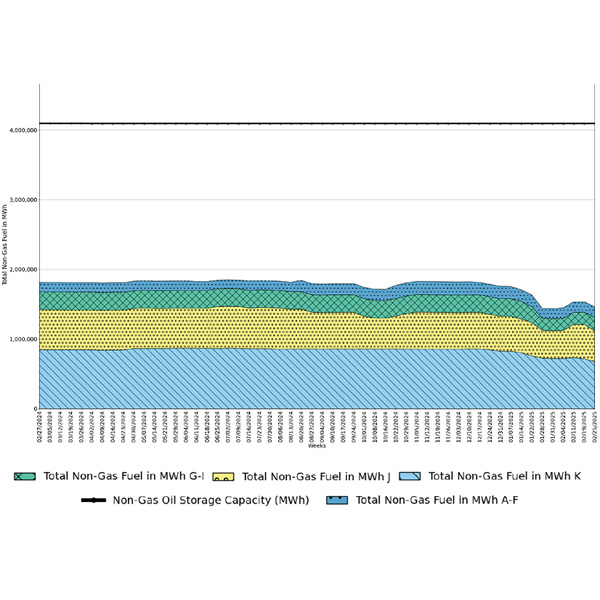
While NYISO operated reliably last winter, the season provided “continued examples of limited flexibility on the gas system,” ISO staff told the Operating Committee.
PJM credited emergency procedures with improving generator performance during a pair of winter storms in January, including a new all-time winter peak of 145,060 MW.
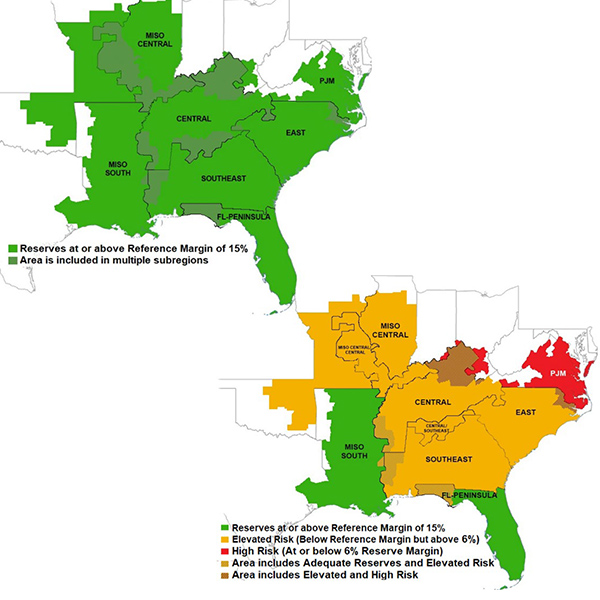
In its Winter Reliability Assessment, SERC Reliability said several of its subregions have high or elevated risk of energy shortfalls during extreme conditions.
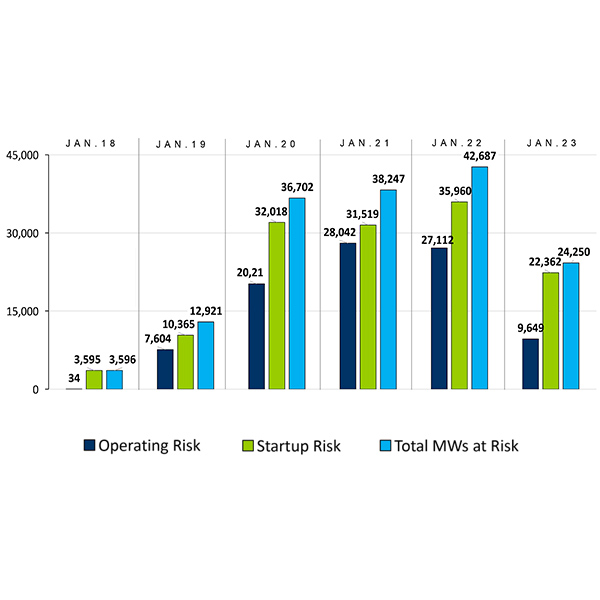
NERC staff said they see both signs of progress and looming challenges in the ERO's winter reliability assessment.
An emergency alert urging the public to conserve energy helped the Alberta Electric System Operator narrowly avert rolling blackouts during January’s extreme cold snap.
PJM spent $53.5 million on conservative, out-of-market dispatch procedures to maintain reliability during the January 2024 Winter Storm Gerri.
ERCOT set a new winter peak during a winter blast that pushed temperatures 30 to 50 degrees below normal in Texas.
Want more? Advanced Search