FERC & Federal
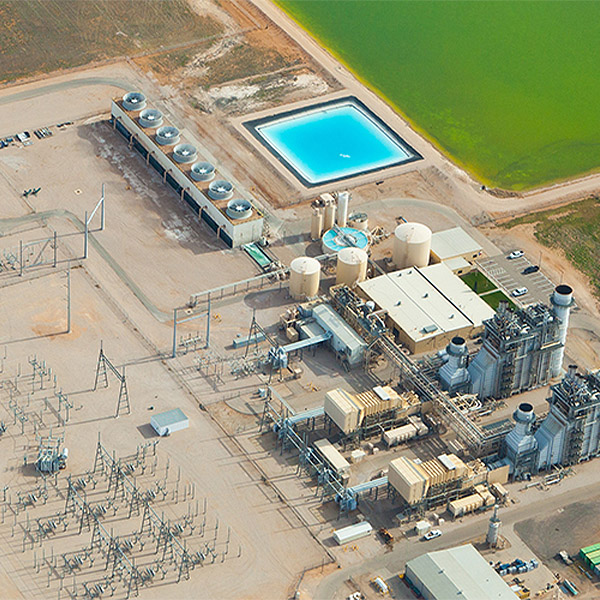
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
Concerns over FERC’s legal authority to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions came up throughout the commission’s technical conference on GHG mitigation.
FERC approved a consent agreement between its Office of Enforcement and Golden Spread Electric Cooperative over charges of market manipulation.
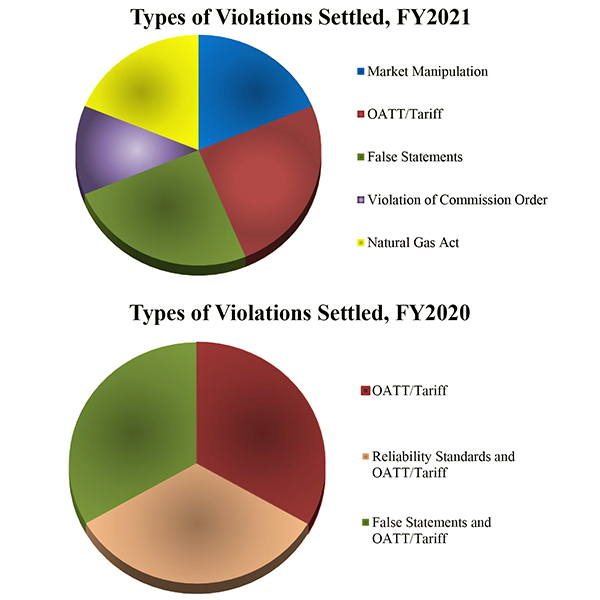
Activity at FERC’s Office of Enforcement opened 12 new investigations and settled nine pending ones for about $7.9 million in fiscal 2021.
FERC approved an inquiry into how reactive power capability should be compensated in the face of changing conditions on the nation’s electricity grid.
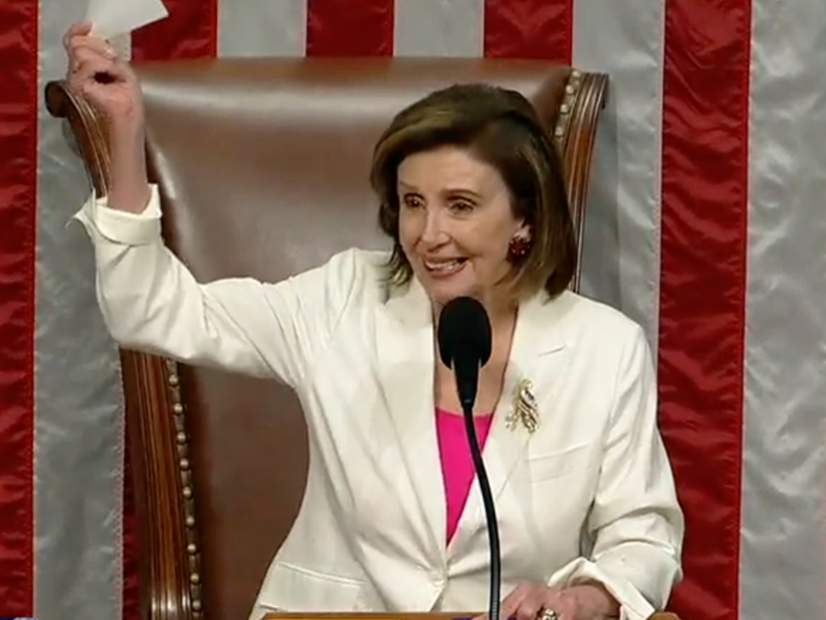
The U.S. House passed the Build Back Better bill, the $1.75-trillion budget reconciliation package that is key to advancing President Biden’s climate agenda.
The Senate unanimously confirmed Willie Phillips to FERC, securing the Democrats a majority on the commission for the first time in more than four years.
Opponents of the recently instituted Southeast Energy Exchange Market are seeking to overturn its approval, granted last month by a deadlocked FERC.
President Biden signed the $1.2 trillion, bipartisan Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, drawing praise from across the energy sector.
FERC Chair Richard Glick said there is “a lot to be done” to build out the transmission grid to handle the clean energy transition.
Utility and RTO officials at NARUC’s annual meeting expressed hope for FERC’s recent ANOPR aimed at improving regional transmission planning.
Want more? Advanced Search