Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
The PUCO ruling seeks to ensure that other ratepayers are not stuck with paying for infrastructure upgrades made to accommodate data center power demand that does not materialize as requested.
How deeply the One Big Beautiful Bill Act will impact clean energy still is being determined.
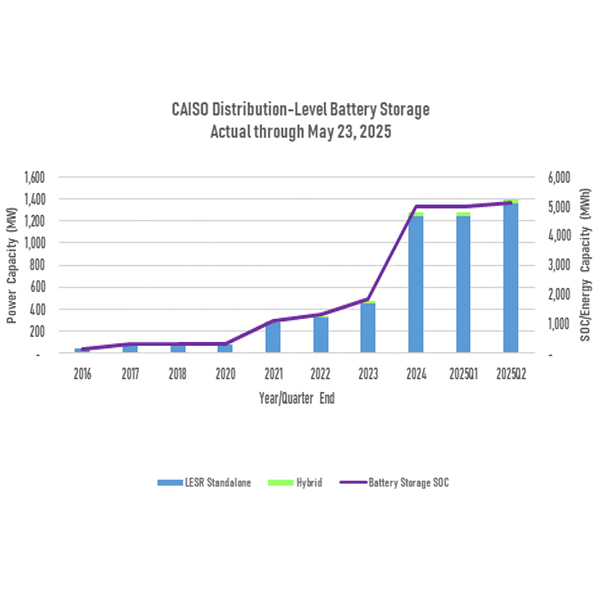
CAISO is working on an initiative to improve the visibility of distributed battery storage resources on the grid, especially for when they are needed for resource adequacy.
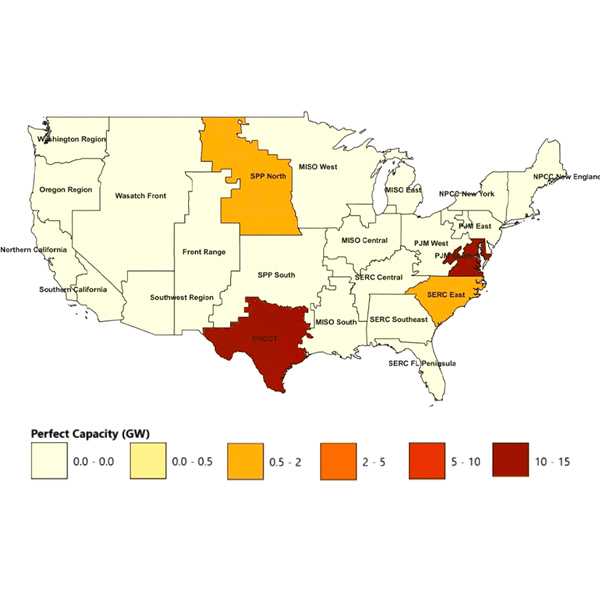
DOE's report tries to apply one reliability metric to different markets and finds significant new capacity will be needed in some markets to avoid reliability problems by 2030.
ISO-NE’s capacity deficiency event demonstrated the significant benefits of solar resources, along with their limits in displacing fossil resources during peak load periods.
A new Clean Energy States Alliance report highlights how states are tackling the rise in electricity demand, which varies based on factors such as the scale of demand growth they face and their geography.
Google is reporting another sharp annual jump in electricity consumption at its data centers but says greenhouse gas emissions were lower in 2024 than 2023, by some measures.
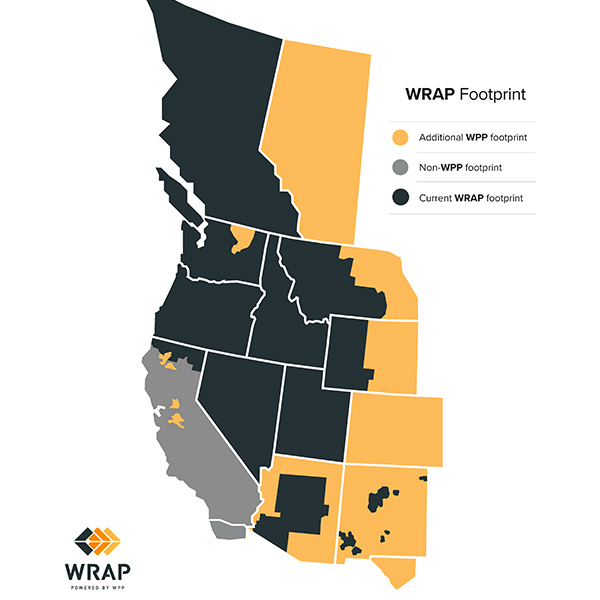
Even in its nonbinding phase, the Western Power Pool’s Western Resource Adequacy Program has been a valuable tool for working toward resource adequacy goals, program participants said.
The House of Representatives voted to pass the Senate version of its budget reconciliation package, the One Big Beautiful Bill Act.
The U.S. Senate met through the weekend and overnight June 30 to work on Republicans’ budget reconciliation bill, passing it 51-50 with Vice President JD Vance casting the tiebreaking vote.
Want more? Advanced Search