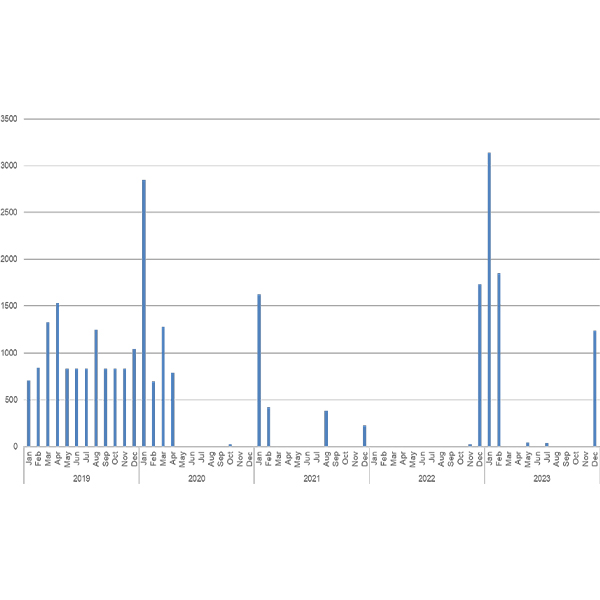
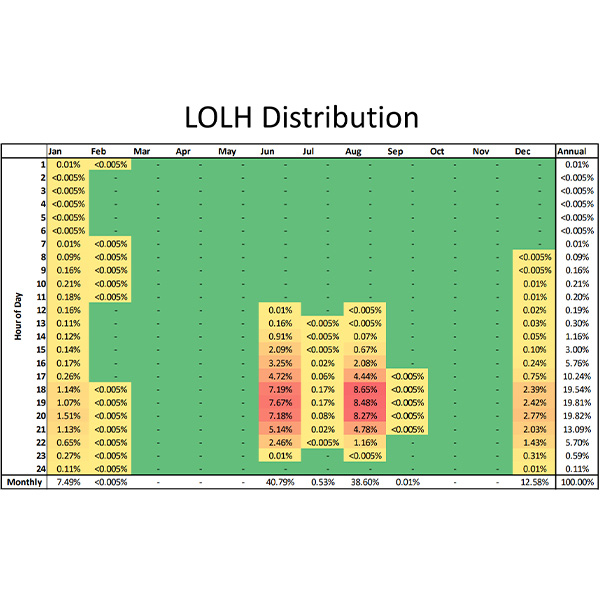
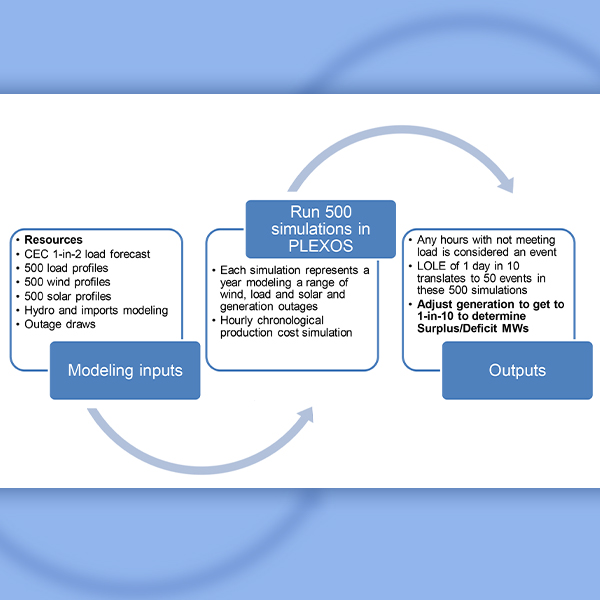
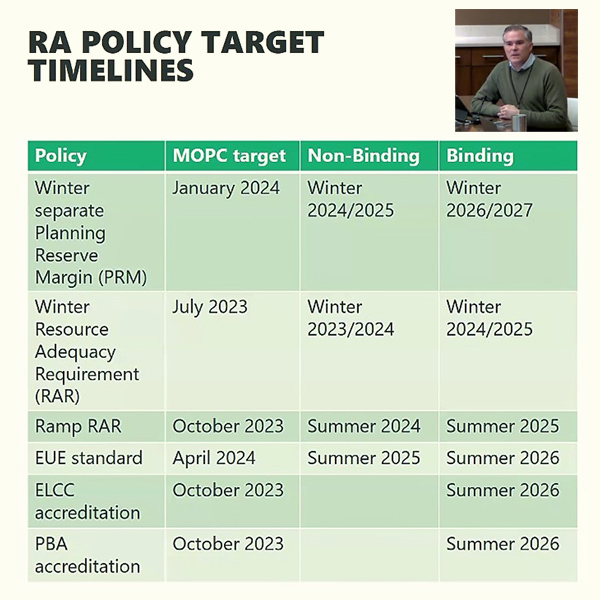
loss of load expectation (LOLE)
Lack of visibility into the contract and availability status of the fleet is causing “inefficiencies” in CAISO’s capacity procurement mechanism process, staff and stakeholders said.
ISO-NE presented the NEPOOL Markets Committee with additional results of the impact analysis for the RTO’s resource capacity accreditation project, which looked at how changes to the resource mix would affect the seasonal distribution of shortfall risks.
SPP’s Resource and Energy Leadership Team marked the one-year anniversary of its formation with yet another discussion of resource adequacy issues and the various metrics used to determine a reliability standard.
CAISO staff and stakeholders again dove into the details of the ISO’s resource adequacy construct, including potentially creating year-ahead requirements and refining the existing capacity procurement mechanism.
SPP REAL Team members conducted a “therapy session” in forming a consensus position around its schedule and priorities for 2024.
SPP stakeholders endorsed a tariff revision request that adds a winter resource adequacy requirement for load-responsible entities bound by the grid operator’s recent planning reserve margin increase.
SPP staff and stakeholders spent much of last week’s virtual Markets and Operations Policy Committee meeting discussing resource adequacy.
FERC accepted revisions to PJM’s tariff that the RTO proposed via its Quadrennial Review of the parameters underlying its Reliability Pricing Model auctions.
The electric sector must fundamentally reconsider how it measures and manages grid reliability, speakers on a WECC panel said.
Texas lawmakers and ERCOT stakeholders did not hold back as they took their first shots at state regulators' proposed redesign of the market.
Want more? Advanced Search