NEPOOL Reliability Committee Briefs: April 22, 2020.)
Black reviewed changes to the gross load forecast reconstitution methodology, which is used to prevent the double-counting of PDRs in the RTO’s Forward Capacity Auction.
PDRs receive compensation as a supply-side resource and reduce demand, thus their demand-reducing impact becomes embedded in historical load data. To ensure that PDRs are not double-counted, the RTO must add — or reconstitute — PDR demand reductions into historical loads used in the development of a forecast of future loads.
EE measures comprise the majority of PDR energy, Black said. However, some EE measures expire, which also requires reconstitution of the load forecast data.
“When we say expiring measures, we’re referring to EE measures that have reached the end of their useful measured life and can no longer participate in FCM as supply,” Black said. “Some of the lingo in the industry is that there will be no backsliding.”
[Note: Although NEPOOL rules prohibit quoting speakers at meetings, those quoted in this article approved their remarks afterward to clarify their presentations.]
ISO-NE will present the load forecasting methodology changes to the RC for an advisory vote in June. Upon approval by NEPOOL’s Participants Committee, the RTO will file the Tariff changes with FERC with a requested effective date of Aug. 30.
The change in load forecasting methodology is the first of three related initiatives the RTO introduced to relevant NEPOOL technical committees so far this year. The second initiative considers the impact of behind-the-meter solar PV on future planning assessments. The third is intended to better integrate the FERC Order 1000 solicitation process into the reliability delist bid review, starting with FCA 15.
Changes to PP10 for Tx Solution
The RC approved changes to Planning Procedure 10 (PP10) to provide implementation details for the alignment of reliability reviews of delist bids with the competitive transmission solution process. It recommended that the PC support the revisions at its next meeting June 4.
ISO-NE Director of Transmission Services and Resource Qualification Al McBride presented the proposed changes to “better describe how responses in the competitive solicitation process that meet certain conditions may be accounted for in the review of rejected delist bids under Section 7.5 of PP10.”
The RTO presented and discussed the proposal at the April 22 RC meeting.
If approved, the changes would not affect the outcomes of the selection processes stemming from Order 1000, nor would they have any effect on how new resources participate in the FCM, McBride said. They are intended to prevent unnecessarily retaining a resource for reliability if transmission responses in the competitive solicitation process address the reliability need.
Metering for DC-coupled Assets
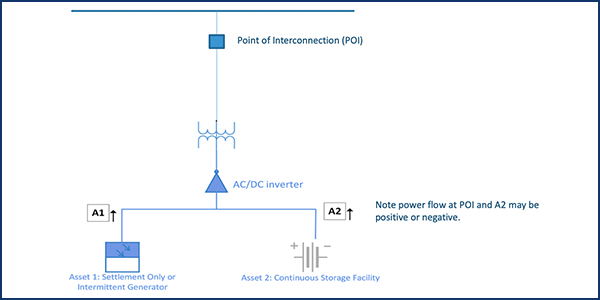
ISO-NE Manager of Demand Resource Administration Doug Smith presented changes to Operating Procedure 18 (OP-18) that would enable DC-coupled facilities to participate in the markets as separate assets. The proposed redline changes attempt to leverage existing processes while ensuring that metering and telemetry for DC-coupled facilities meet the same standards that apply to other generating facilities.
The RTO proposes the changes become effective in the third quarter because some DC-coupled facilities are likely to be commercial by then. Several market participants are installing electric storage and intermittent generation behind the same point of interconnection. Some of those “co-located” facilities are DC coupled, meaning that both the storage and intermittent components share one or more inverters, thus the need to address the metering of such assets.
ISO-NE will bring the matter back for an advisory vote in June.
Committee Actions
The RC’s notice of actions included approval of several motions, noting that all sectors had a quorum.
The committee approved a cluster of projects in Western Massachusetts for National Grid (NEP-20-G03), including 96 state-jurisdictional projects and 19 associated transmission power purchase agreements.
National Grid also won approval for a cluster study in Rhode Island (NEP-20-G04), composed of 39 state-jurisdictional projects and two associated transmission PPAs.
The RC approved a pool transmission facility (PTF) cost allocation of $375 million to Eversource Energy for transmission upgrade costs on 27 separate projects in Connecticut, Massachusetts and New Hampshire.
Eversource also had $7.5 million in PTF cost allocations approved for work associated with the replacement of 25 wooden structures on the 345-kV 371 line and $11.8 million in PTF cost allocation approved for work associated with the replacement of 55 wooden structures on the 345-kV 321 line.
The RC also approved a revision to Operating Procedure 12 (OP-12) related to voltage and reactive control, recommending that the PC support the revisions at its June 4 meeting.