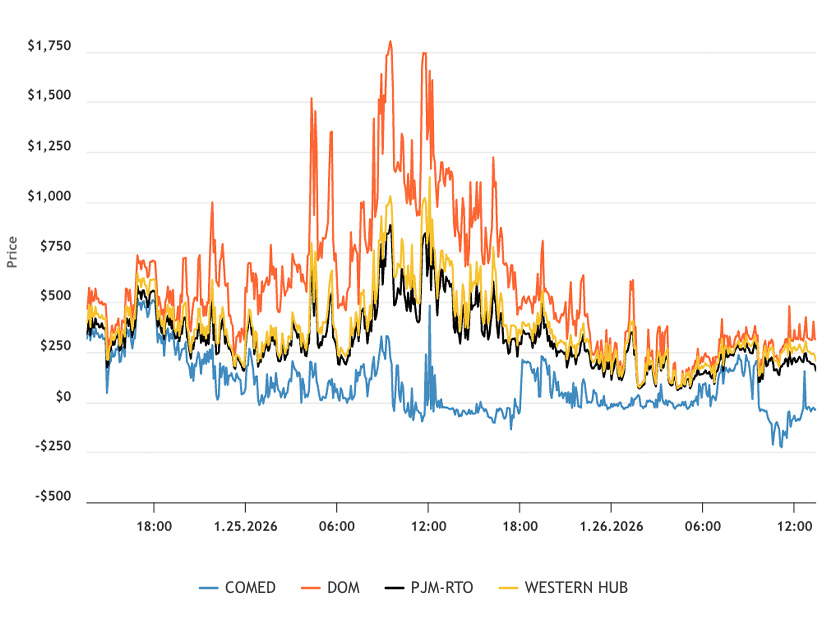
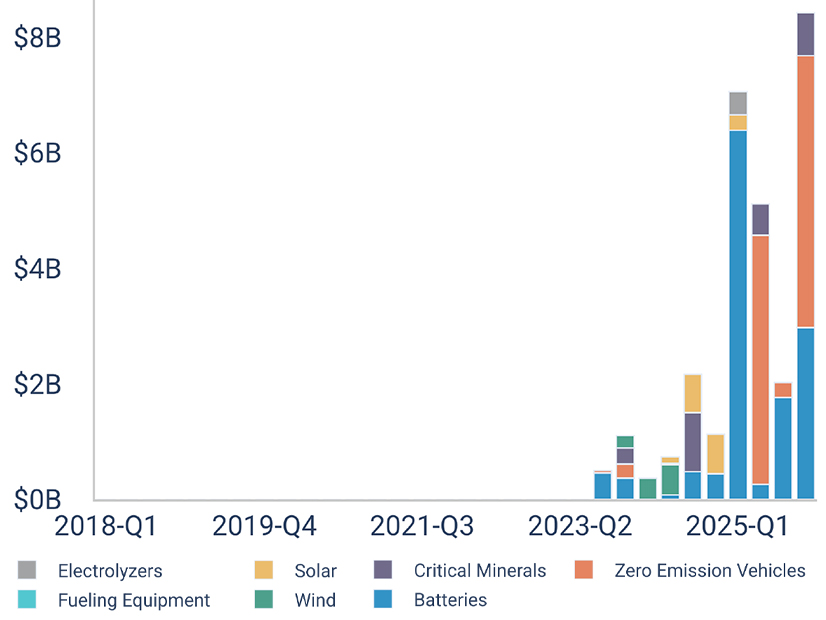
NERC and other stakeholders have endorsed FERC’s proposal to introduce new standards to improve coordination between the electric and natural gas industries, with some commenters urging the commission to go further in support of grid reliability.
Commenters were responding to FERC’s Notice of Proposed Rulemaking from October 2025 that would incorporate the latest changes to Version 4.0 of the Standards for Business Practices of Interstate Natural Gas Pipelines adopted by the Wholesale Gas Quadrant of the North American Energy Standards Board (NAESB) (RM96-1). (See NOPR Would Get Pipelines to Offer More Information for Grid Operators.)
NAESB’s updates include a revised standard that creates a central location on pipeline websites for information on critical events that RTOs and ISOs can use to assess potential impacts to their systems. Two new standards would facilitate the posting of applicable scheduled quantity information for power plants that are directly connected to gas pipelines and support the inclusion of geographic information of affected areas, locations and/or pipeline facilities by a transportation service provider when issuing a critical notice.
In its comments, NERC called the commission’s proposal “critical for reliable operations of both [the] gas and electric systems, providing a common platform for operational data exchange and unified situational awareness.” Observing that “the electricity sector is the largest consumer of natural gas,” the ERO highlighted its own efforts to promote gas-electric coordination.
These include NERC’s Electricity-Natural Gas Work Plan, presented to the organization’s Board of Trustees in August 2025. As part of the plan, NERC has updated its Long-Term Reliability Assessments to include natural gas impacts on grid reliability and is “reviewing updates to its tool for Situational Awareness for FERC, NERC and the regional entities … to better integrate gas system data.”
NERC also mentioned several reliability standards intended to address natural gas fuel issues, including EOP-011-4 (Emergency operations) and TOP-002-5 (Operations planning), both approved by the commission in 2024, along with TPL-008-1 (Transmission system planning performance requirements for extreme temperature events), BAL-007-1 (Near-term energy reliability assessments) and EOP-012-3 (Extreme cold weather preparedness and operations).
Other electric stakeholders joined NERC to back the commission’s proposal. The ISO/RTO Council wrote that the NAESB standards would “provide more timely and actionable information about gas system constraints and disruptions that may impact electric system reliability” while enabling “more effective coordination of operational decisions across the gas-electric systems.”
National Grid, Consolidated Edison, Old Dominion Electric Cooperative and Washington Gas Light — filing jointly as the Utility Coalition — called NAESB’s standards “a meaningful advancement toward enhancing real-time operational transparency across” the gas and electric systems. But the utilities also suggested the commission “widen its aperture to … consider steps that can be taken to preserve and enhance interstate pipeline service reliability.”
These suggested steps include requiring annual reports from interstate pipelines on reliability metrics, revising its pipeline force majeure policy and reservation charge crediting policy to create reliability incentives for pipelines, and implementing “greater standardization of pipeline scheduling and confirmation practices.” The coalition added that the commission could direct additional modifications to NAESB’s standards to address pipeline reliability.
The American Gas Association also expressed support for adopting the NAESB standards, which it said would “promote greater gas-electric coordination and situational awareness during severe weather events.” AGA suggested possible future steps to further improve communication between the gas and electric industries, including updating the force majeure provisions, as the Utility Coalition said, and promoting investment in gas storage and demand response programs.
Finally, the Interstate Natural Gas Association of America endorsed adoption of the NAESB standards but requested the commission ensure its final rule in the proceeding is timed so the effective date of the modifications “does not occur during the winter heating period.” The association also asked that pipelines be allowed “the flexibility to implement the modifications on or before 180 days from the date compliance filings are due in this proceeding.”