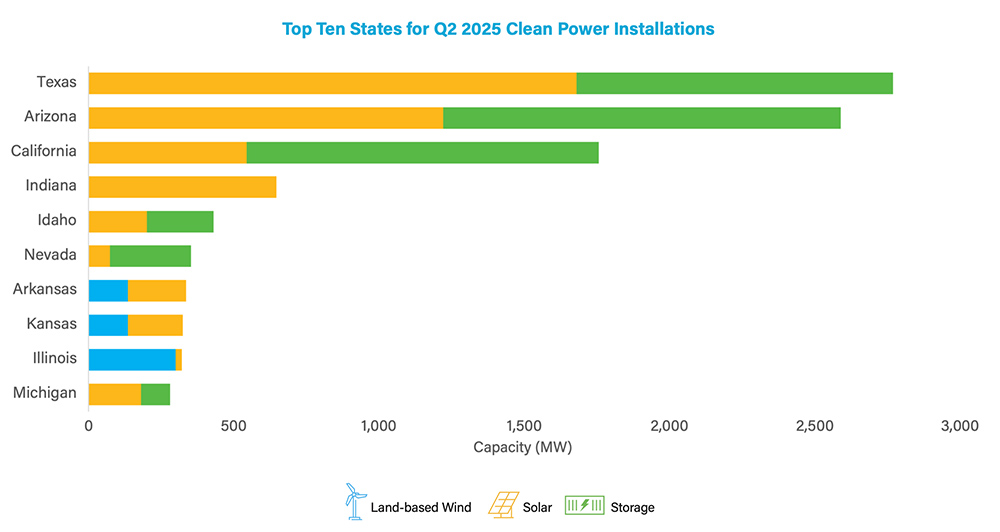
SPP has hinted to members that its 2025 transmission planning assessment will be another large one — larger, even, than last year’s record $7.65 billion package.
One of the drivers is a draft 765-kV overlay that staff and members have been engaged with. It builds on SPP’s first 765-kV project that was approved as part of the 2024 assessment, Southwestern Public Service’s 354-mile transmission line crossing the New Mexico-Texas border. (See SPP Stakeholders Endorse Record $7.65B Tx Plan.)
Casey Cathey, the RTO’s vice president of engineering, shared the overlay during a Sept. 3 education session with the Board of Directors and Regional State Committee.
“What we have done is a preliminary look based on the [Integrated Transmission Planning] loads that the members have provided us,” Cathey said.
The draft overlay extends from SPS’ Potter-Crossroads-Phantom line into Oklahoma, where much of the state would be encircled. Another 765-kV line would shoot off to the Southeast and into Louisiana, the site of two load shed events in April. (See SPP Addresses 3rd Load Shed Since March 31.)
Looking ahead, the 2026 ITP is considering a 765-kV radial line that connects Kansas with North Dakota. One option would close the loop on the western side of the footprint.
“The 2026 plan is going to be a much more detailed engineering analysis, so it may not look exactly like this next year,” Cathey said.
Pointing to large loads “peppered throughout” the map, he said that will “necessitate a version of a 765 footprint.”
“I’m giving some caveats here because there’s a lot of engineering connection points that we may need to change from a reliability perspective,” Cathey said. “However, we are seeing the need for some version of what this looks like moving forward.”
One reason the time is now ripe for 765-kV transmission in SPP’s footprint is the 345-kV build that members have undertaken in recent years. Cathey said the 345-kV backbone gives staff options that didn’t exist 15 years ago to sustain the transfers necessary should a 765 line be lost.
SPP has increased its 765-kV line costs from $4.2 million/mile to $5.8 million/mile, comparable to ERCOT’s and MISO’s projections for their 765-kV projects.
“This is consistent. We’ve gotten some recent feedback from our membership that this is the right way to go and then that the costs are making more sense,” Cathey said. “We don’t have 765 in this region, but it’s been built before. We need to recognize that some things are going to come up. This is going to be pricey. We need to make sure that we’re going into it with eyes wide open.”
The SPS project was awarded in February with an estimated cost of $1.69 billion. SPS filed a revised cost estimate of $3.62 billion in June, more than double the earlier projection and easily outside the variance bandwidth of +/30% that can lead to a re-evaluation. SPP has said the project still is viable, despite its cost. (See SPP Board Sets Aside 765-kV Costs, Large Load Policy.)
The RTO has scheduled an education session on the 2025 ITP for the Markets and Operations Policy Committee meeting Sept. 23. The assessment and its portfolio will be brought before MOPC, state regulators and the board in October and November for their approvals.